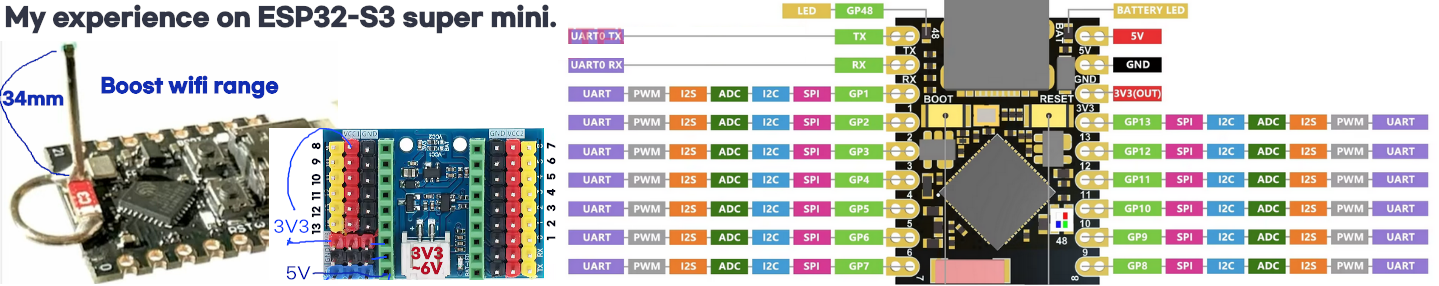
Data Route
2025.10.02 18:06
Q : How to route data between several ESP32 with ESP-NOW-LR mode for mesh network for obstruct zone communication?
Routing data between multiple ESP32 devices in an ESP-NOW-LR mesh network for obstructed zone communication requires a store-and-forward mechanism and a routing protocol. ESP-NOW-LR (Long Range) provides enhanced range, but routing is not inherent to the ESP-NOW protocol itself.
Here is a method for achieving this:
1. Network Topology and Node Roles:
-
Establish a mesh where each node can communicate with its direct neighbors using ESP-NOW-LR.
-
Designate certain nodes as "routing nodes" that actively participate in forwarding messages to their intended destinations, especially across obstructed zones where direct communication is not possible.
-
These nodes primarily send and receive data, relying on routing nodes to deliver messages across the mesh.
2. Routing Protocol Implementation:
-
Packet Structure:Define a custom data structure for your messages that includes:
- Source MAC Address: The MAC address of the originating node.
- Destination MAC Address: The MAC address of the intended recipient node.
- Hop Count (Optional): To prevent infinite loops and track path length.
- Payload: The actual data being transmitted.
-
Discovery and Neighbor Management:
- Each node should maintain a list of its directly connected neighbors (their MAC addresses).
- Periodically, nodes can broadcast "hello" messages to discover new neighbors and update their neighbor lists.
-
Routing Table:Each routing node should maintain a routing table that maps destination MAC addresses to the next-hop neighbor (the MAC address of the neighbor to which the packet should be forwarded to reach the destination).
-
Packet Forwarding Logic:
- When a node receives a packet, it checks the destination MAC address.
- If the packet is for the current node, it processes the payload.
- If the packet is for another node, the current node consults its routing table to determine the next hop.
- The packet is then forwarded to the next-hop neighbor using ESP-NOW-LR.
- If no route is found, the packet might be dropped or a route discovery process initiated.
-
Route Discovery (Dynamic Routing):
- When a node needs to send data to an unknown destination, it can initiate a route discovery process (e.g., a limited broadcast of a route request packet).
- Intermediate nodes receiving the route request can reply with their own routes to the destination, or forward the request further.
- The originating node selects the best route (e.g., shortest hop count).
3. ESP-NOW-LR Specific Considerations:
-
Broadcast for Discovery:Use the broadcast MAC address (
FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF) for initial neighbor discovery and route requests within the ESP-NOW-LR range. -
Unicast for Data Transfer:Once routes are established, use unicast ESP-NOW messages to send data directly to the next-hop neighbor in the routing path.
-
Error Handling:Implement mechanisms to handle failed transmissions (e.g., retransmissions, alternative route selection).
Example Code Snippet (Conceptual):
C++
// Example of a custom data structure for routing
typedef struct {
uint8_t sourceMac[6];
uint8_t destMac[6];
uint8_t payload[250]; // Max payload for ESP-NOW
// Add other routing info like hop count if needed
} esp_now_routed_message_t;
// Function to send a routed message
void sendRoutedMessage(uint8_t *destMac, uint8_t *data, size_t len) {
esp_now_routed_message_t message;
// Populate message.sourceMac with current node's MAC
// Populate message.destMac with destMac
// Copy data to message.payload
// Determine next hop based on routing table or discovery
uint8_t nextHopMac[6];
// ... (routing logic to find nextHopMac) ...
esp_err_t result = esp_now_send(nextHopMac, (uint8_t *)&message, sizeof(message));
// Handle result
}
// Callback function for receiving messages
void OnDataRecv(const uint8_t *mac_addr, const uint8_t *incomingData, int len) {
esp_now_routed_message_t *receivedMessage = (esp_now_routed_message_t *)incomingData;
// Check if message is for this node
if (memcmp(receivedMessage->destMac, myMacAddress, 6) == 0) {
// Process received data
} else {
// Forward the message based on routing table
sendRoutedMessage(receivedMessage->destMac, receivedMessage->payload, sizeof(receivedMessage->payload));
}
}
Comment 0
| No. | Subject | Author | Date | Views |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Notice | For the first time user of ESP32-S3 super mini users. | me | 2025.04.25 | 1204 |
| 16 | Other Approach proposed by Gemini | me | 2025.10.02 | 513 |
| » | Data Route | me | 2025.10.02 | 547 |
| 14 |
Extra Hardware Serial + JSON servo control
| me | 2025.09.22 | 397 |
| 13 |
Wheel Arc movement with continous servos
| me | 2025.09.21 | 368 |
| 12 |
3 Servo Test
| me | 2025.09.21 | 352 |
| 11 |
Object Pascal App getting data from ESP32-S3 (Parsing)
| me | 2025.04.29 | 820 |
| 10 |
Sound Sensor Test
| me | 2025.04.27 | 850 |
| 9 |
Laser distance sensor VL53L0X
| me | 2025.04.27 | 879 |
| 8 |
9DOF : Getting Pitch & Roll with ICM20948 v2
| me | 2025.04.27 | 861 |
| 7 |
Formating output
| me | 2025.04.27 | 812 |
| 6 | Blinking Built-in RGB without delay() | me | 2025.04.25 | 5696 |
| 5 | Built-in RGB led Demo | me | 2025.04.25 | 994 |
| 4 | Servo Demo | me | 2025.04.25 | 811 |
| 3 |
HMC5883L Compass demo
| me | 2025.04.25 | 1019 |
| 2 |
I2C Address Search
| me | 2025.04.25 | 874 |
| 1 |
Serial Sample (ASCII Table)
| me | 2025.04.25 | 997 |
